CLINICAL PRESENTATION
A 12yo African American male presented to the Howard University, College of Dentistry, Department of Orthodontics, for evaluation. The patient showed a skeletal and dental class III occlusion with generalized anterior spacing. The facial profile displayed profound convexity while his frontal analysis displayed symmetry in all planes (vertical and transverse). His cephalometric analysis confirmed the skeletal anomaly (class III), with proclined upper incisors. The patient was referred to Martin D. Levin, DMD, Bethesda-Chevy Chase Root Canal Specialists, for endodontic evaluation and possible CBCT.
CLINICAL DESCRIPTION
Right side of maxilla: Lesion can be palpated on the palatal surface between the lateral incisor and cuspid. Lesion was elevated- approximately 3 mm of elevation and approximately 23 mm x 7 mm in surface dimension, is ovoid, circumscribed, well defined, with no variation in color, and fluctuant under pressure; no pain upon palpation and non-symptomatic. Palatal bone plate cannot be palpated between the maxillary right lateral incisor and cuspid.
The maxillary left teeth tested normally to percussion, palpation, bite-stick, electric pulp test, thermal, periodontal, mobility and were normal color. Patient denied history of trauma.
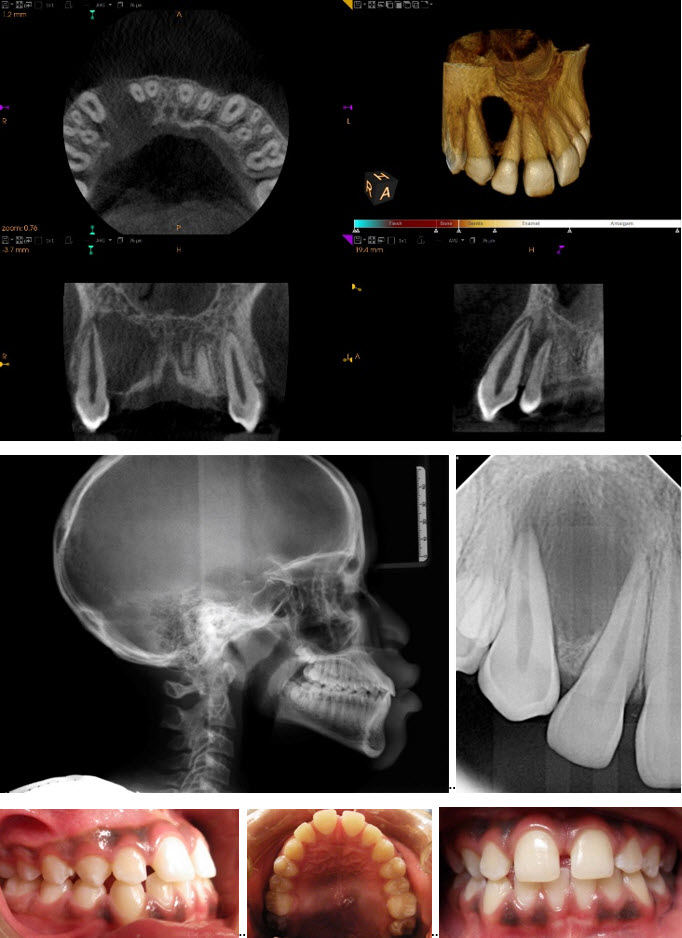
RADIOGRAPHIC DESCRIPTION OF LESION
- Location: maxillary right anterior alveolus, between roots from CEJ to the apex of teeth #s 6 and 7
- Radiodensity: low density
- Size: Approx. 18.0 mm x 15.0 mm
- Shape: unilocular/ovoid
- Borders: partially well-defined mesial to canine between the maxillary right lateral incisor and cuspid non-corticated; poorly defined between distal teeth maxillary right central and lateral incisor
- Internal architecture: uniform low density
- Effect on surrounding tissues: lesion has locally destroyed buccal and palatal cortical plates of the right anterior side of maxilla with 6 mm of expansion of buccal and palatal plates in the area between the right lateral incisor and cuspid; no lamina dura observed in associated tooth roots adjacent to lesion; roots of the maxillary right lateral incisor and cuspid were displaced mesially and distally respectively; thickening of the membrane of the floor of the maxillary sinus (3-5 mm within the field of view) Maxillary Sinuses show uniform, 3 mm–5 mm thickening of the mucous membrane of the floor within the image volume
(The listed structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry, configuration, cortical outline, medullary space, and patent sinuses/airways. Evaluation of the CBCT anatomical volume is intended as an overall review for pathology and abnormalities not directly associated with dental and periodontal conditions best imaged by conventional dental radiography. All viewed structures determined to have no significant findings are reported as no abnormalities detected.)
IMPRESSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Maxillary right: features consistent with a lateral periodontal cyst, keratocystic odontogenic tumor, or central giant cell granuloma; referral to oral and maxillofacial surgeon for evaluation and possible treatment of maxillary right alveolar lesion (including biopsy) between the maxillary right lateral incisor and cuspid.
(The purpose of this image examination is to provide an evaluation of the regional anatomical volume not directly involved with the specific intent of the imaging examination. Evaluation is limited to the capability of CBCT imaging and any further assessment of dental related conditions is best performed by conventional dental radiography. This is a consultative report only and is not intended to be a definitive diagnosis or treatment plan.)
Attending Resident: Rina Gonzalez-Albazzaz, DMD
Consulting Orthodontist: Sana Augustus, DDS
Consulting Radiologist: Barry Pass, DDS, PhD
Consulting Endodontist: Martin D. Levin, DMD